Overview of AI Agents
An AI agent is an autonomous software program designed to interact with its environment, collect data, and perform self-directed tasks to achieve predefined goals. Unlike traditional software, AI agents operate independently by making decisions, planning actions, and adapting based on new information without constant human intervention. Key characteristics include autonomy, goal-oriented behavior, perception through data collection, rational decision-making, proactivity, continuous learning, adaptability, and collaboration with other agents or humans. At their core, AI agents often rely on large language models (LLMs) such as GPT or Claude, which enable them to interpret natural language, reason over complex instructions, and interact with external tools and APIs. AI agents are widely used to automate complex workflows, enhance productivity by handling repetitive tasks, reduce operational costs, improve decision-making through real-time data analysis, and elevate customer experiences with personalized, efficient service.Training Data
There are two primary types of training data used to build AI agents:-
Websites
Training data can be sourced by providing URLs of websites. The system crawls these URLs to extract relevant text content for training. This method leverages publicly available web content and requires only the input of URLs by the user. -
PDFs
Users upload text-based PDFs to contribute training data. It is important to upload only searchable, text PDFs (not image-based PDFs) to ensure reliable data extraction. Uploading unsupported PDF formats will cause training failures.
Proper data preparation is crucial to ensure the AI agent is trained effectively and accurately.
What is Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)?
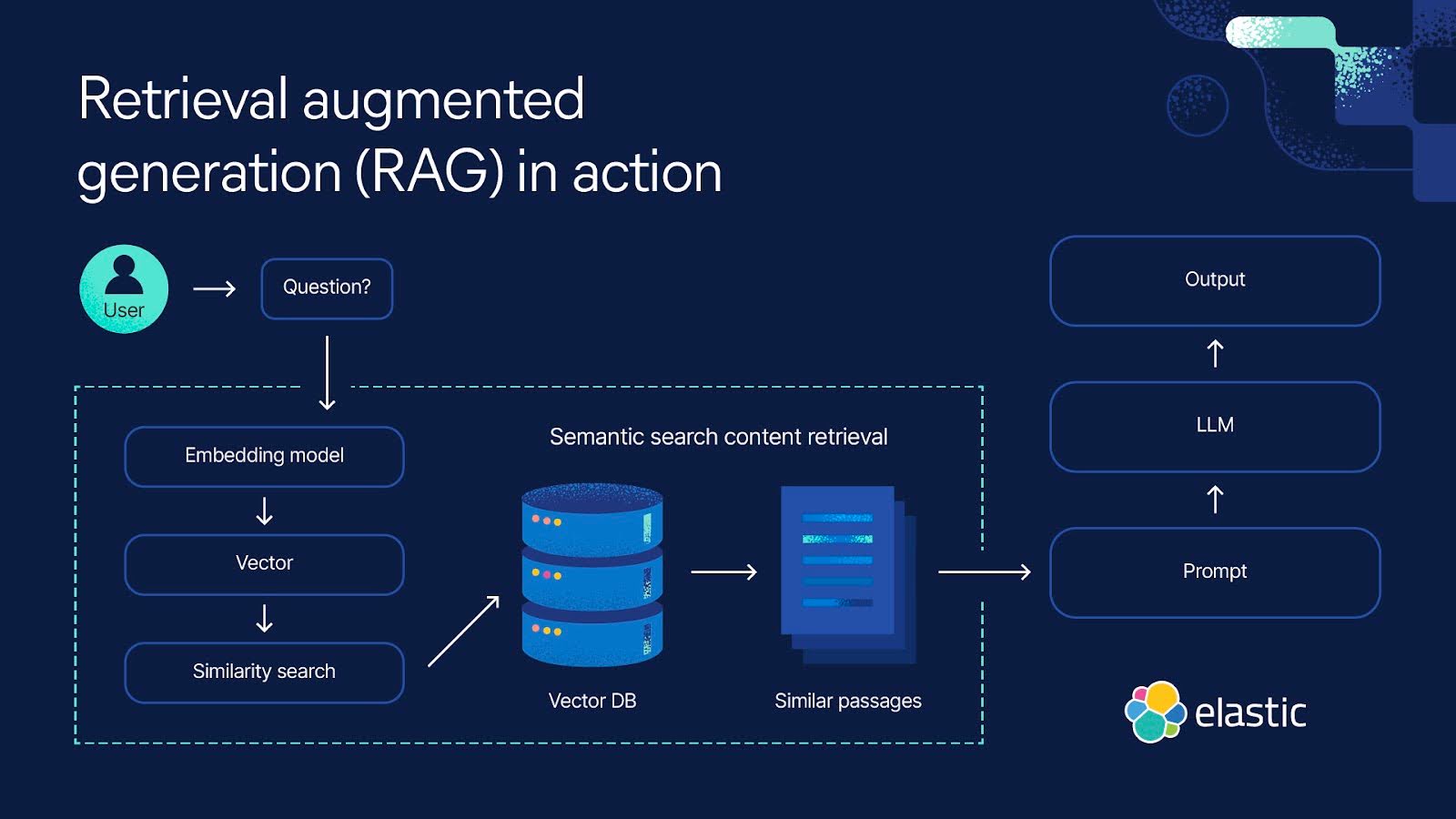
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a method that enhances Large Language Models (LLMs) by augmenting their output with relevant information retrieved from an external knowledge base at query time. This approach compensates for the static knowledge limitation of LLMs, which are infrequently retrained and may have outdated information.How RAG Works:
- A user poses a query.
- The system searches a knowledge base — often a vector database containing text their numerical embeddings — to find context relevant to the query.
- The retrieved context is added to the query prompt sent to the LLM.
- The LLM generates a response informed by both its training and the retrieved context.
Use Cases:
- Answering questions using up-to-date documents or company-specific data.
- Improving natural language processing tasks with fresh contextual information.
- Incorporating relevant images or visual data in multimodal applications.
Steps to Create an Agent
- Navigate to https://app.leadsai.in/agents.
- Click “Create Agent”
- Provide the agent’s name, description, and system prompt.
- Upload PDFs (text-based only) and enter website URLs.
- Click “Create Agent” to start training.
Common Errors
- Website unreachable: The provided URL cannot be accessed.
- PDF unreadable: The uploaded PDF is corrupt or in an unsupported format.
- Invalid PDF format: Only text-based PDFs are supported; image-only PDFs will cause failure.
Updating Agents
Agents can be updated in two ways:- Basic Info Update: Modify the agent’s name, description, or system prompt by saving basic information without retraining.
- Full Re-training (Save All Changes): Deletes the agent’s existing data and retrains it from scratch using new data sources. Note: Only 3 full trainings are allowed per workspace per week.
Deleting Agents
Deleting agents is not allowed, as live users may be linked to these agents.
